|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Geometrically nonlinear configurations of thin elastic rods (this and the next slide) |
|
|
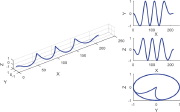
| Helical buckling of an axially compressed beam confined in an elliptical cylinder |
|
| Geometrically nonlinear configurations of thin elastic rods (this and the previous slide) |
|
| Dynamic buckling: Elastic strip is stretched, then released |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
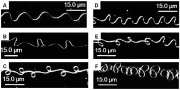
| Buckled patterns created from electrified jets of polyethylene oxide collected on glass slides |
|
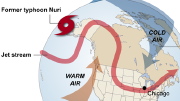
| November 10, 2014: Buckled jet stream brings warm air and cold air |
|
| September 11, 2012: Jet stream buckles over Chicago, giving rise to a pocket of unusually cold, unstable air aloft. |
|
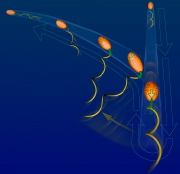
| Marine microbe changing swimming direction via a high-speed buckling of flagellum base (green) |
|
| Thermal railroad track buckling (from Wikipedia) |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|
| Buckled railroad track (from differential thermal expansion of the track versus the bed |
|
| Buckling of a road due to earthquake displacements in California |
|
| Tacoma Narrows bridge failure due to flutter |
|
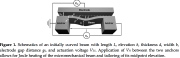
| Bistable voltage-actuated switch |
|
|