|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
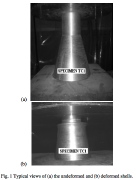
| Axially compressed metallic cylinder-cone combination tested under uniform end shortening |
|
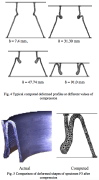
| Top: Comparison of results from test and computational model for axially compressed cylinder-cone shell; Bottom: The configuration |
|
| Axisymmetric deformation of the cylinder-cone combination under uniform end shortening |
|
| Explosive charge set off near a Naval ship USS Winston S. Churchill (DDG 81) |
|
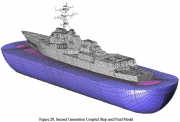
| Discretized ship and fluid |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
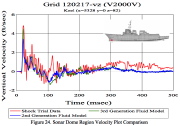
| Dynamic response from the shock: Vertical velocity versus time from test and simulation for a point in the sonar dome region |
|
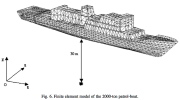
| A discretized 2000-ton patrol boat with a 576 lb charge of TNT placed 30 m directly underneath the keel |
|
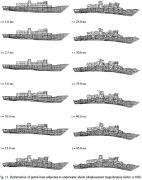
| Deformation of the 2000-ton patrol boat subjected to underwater shock |
|
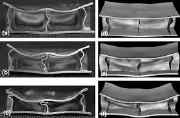
| Fig. 13. The plastic zone progress of the patrol-boat subjected to underwater shock. |
|
| Buckling of shock-loaded metallic sandwich beam. The shock loading is normal to the upper face sheet of the sandwich. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
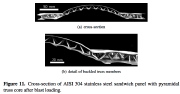
| Blasted sandwich plate with pyramidal core. The shock loading is normal to the lower face sheet of the sandwich. The entire assembly is initially flat. |
|
| A compound pressure vessel composed of isogrid-stiffened shell segments |
|
| Compound shell structure for a bridge |
|
| Three thin-shell tank structures |
|
|
|