|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Buckling of silos under various loadings |
|
| Buckling of large steel tanks |
|
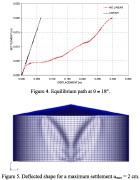
| Buckling of storage tank due to uneven ground settlement |
|
| Liquid storage tanks are constructed in courses, each course of constant thickness and course thickness increasing from top to bottom |
|
| Horizontal ground motion during 1986 El Salvador earthquake and Fourier amplitude spectra |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
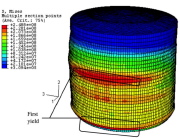
| von Mises stress distribution in the tallest tank shown 2 slides ago in response to the 1986 El Salvador earthquake spectrum with PGA = 0 |
|
| Buckling near the top of the tank shown in the previous slide. This buckling mode is caused by local dynamic circumferential compression from liquid sloshing during the earthquake. |
|
| Cone-roofed step-walled tanks to be subjected to uniform external pressure |
|
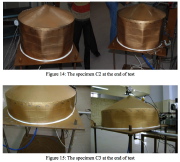
| Preparation of Specimen C3 and Specimen C1 after testing |
|
| Specimens C2 and C3 after testing |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
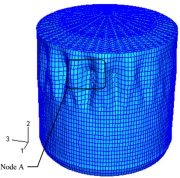
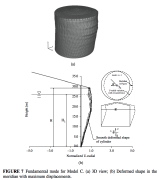
| Prebuckling deformation of the tank shown in (c) 4 slides back during the El Salvador earthquake |
|
| Prebuckling deformation of the tank shown in (b) 5 slides back during the El Salvador earthquake |
|
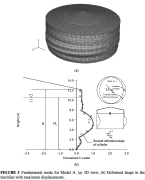
| Prebuckling deformation of the tank shown in (a) 6 slides back during the El Salvador earthquake |
|
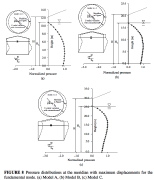
| Pressure distributions from the liquid in the 3 tanks |
|
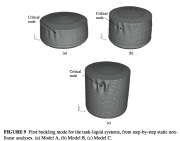
| Fundamental buckling modes of the three liquid-filled tanks |
|
|