|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
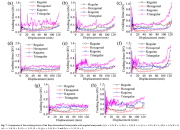
| Axial force - axial displacement curves for various types of honeycombs |
|
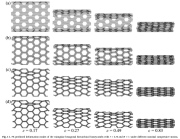
| Finite element models of axial crushing of the triangular hexagonal hierarchical honeycomb for 4 values (a,b,c,d) of side-length ratio, r |
|
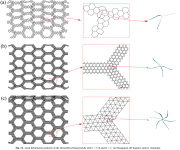
| Local ("micro") buckling of individual cell side-walls occurs during the overall axial crushing process |
|
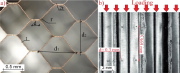
| Compression of honeycomb in the plane of the cell walls |
|
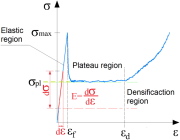
| Fig. 9. The typical compression response of cellular materials. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
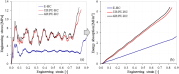
| (a) Stress-strain and (b) Energy absorption-strain of three types of honeycomb |
|
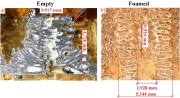
| Crushed (a) empty and (b) foam-filled honeycombs |
|
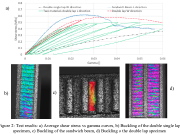
| Shear stress vs shear angle Gamma |
|
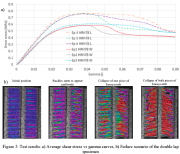
| Shear stress vs Gamma for a double lap specimen |
|
| Initial shear buclking of double-lap sandwich core |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
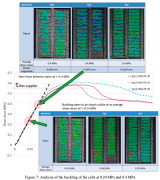
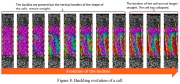
| Shear buckling of a single cell of the honeycomb core |
|
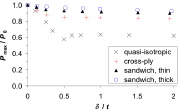
| Buckling load vs imperfection amplitude for axially compressed sandwich cylindrical shells |
|
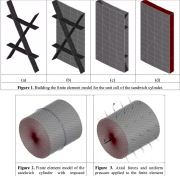
| Hydrostatically compressed lattice-core sandwich cylindrical shell |
|
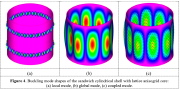
| Buckling modes of the hydrostatically compressed lattice-core sandwich cylindrical shell with construction shown in the previous image |
|
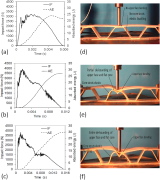
| Low-velocity impact normal to the surface of a sandwich structure with a corrugated core |
|
|