|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
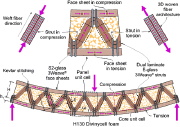
| Bending of truss-core sandwich panel |
|
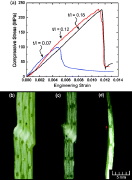
| Typical response of a truss member (called "strut"): (a) Compressive stress-strain; (b-d) 2 types of buckling |
|
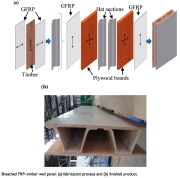
| Truss-core sandwich construction from various different materials |
|
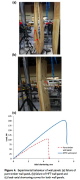
| Test specimens buckled under uniform axial compression: (a) plywood only, (b) compound material as in the previous image, (c) load-end shortening curves |
|
| Nonlinear indentation of a skin resting on a foam substrate |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
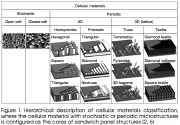 |
|
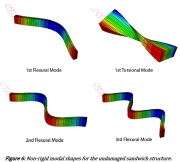
| Vibration modes of a sandwich structure |
|
|
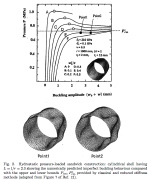
| Load-deflection curves of imperfect sandwich cylindrical shells under external hydrostatic pressure |
|
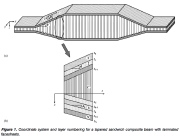
| Truss-core sandwich panel with plywood face sheets |
|
| Various sandwich wall constructions |
|
|
|
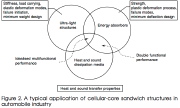 |
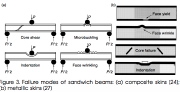 |
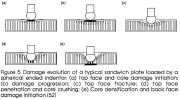 |
 |
 |
|
| Why use sandwich wall construction in the automobile industry? |
|
| Various types of sandwich wall failure that might be caused by local indentation |
|
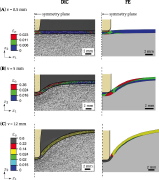
| Progressive damage during local sandwich wall indentation |
|
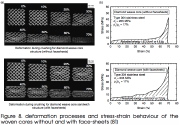
| Crushing of a particular sandwich core without and with face sheets |
|
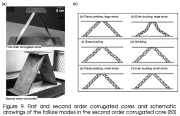
| Truss core modes of deformation when each truss member is itself a mini-truss-core sandwich |
|
|