|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
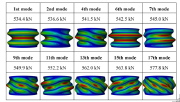
| Buckling modes of an axially compressed laminated composite cylindrical shell with a sandwich wall |
|
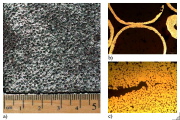
| The sandwich core foam consists of tiny steel spherical shells: a) overall interior foam, b) contact between spheres, c) foam core is not fully dense. |
|
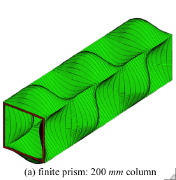
| Buckling mode of an axially compressed box tube with the type of foam-core sandwich wall shown in the previous slide |
|
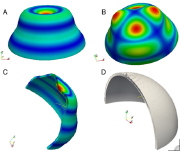
| Various buckling modes of an externally pressurized spherical shell with a sandwich wall construction |
|
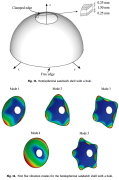
| Vibration of hemispherical sandwich shell |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
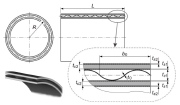
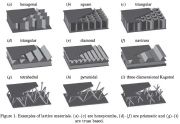
| Fig. 1. The cross section of the wall of a seven-layer cylindrical shell with a circumferentiallly oriented corrugated core |
|
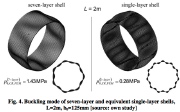
| Comparison of predictions from 7-layer model (previous slide) with the equivalent single-layer model |
|
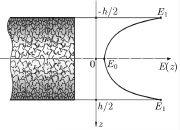
| Variation of the elastic modulus E through the thickness of a sandwich plate with a porous wall |
|
|
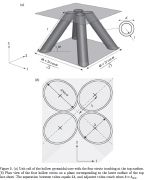
| Sandwich core with pyramidal tubes. The compresive loading is normal to the surface of the sandwich assembly. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
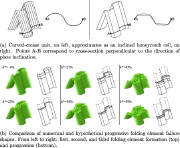 |
 |
|
| Different sandwich core buckling modes from test and theory. |
|
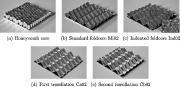
| Five types of sandwich cores that can be crushed by impact normal to the upper face sheet, which is removed in this picture. |
|
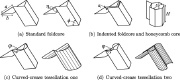
| Honeycomb sandwich core and various inclined core geometries |
|
| Single-cell sandwich core geometries and their typical modes of crushing |
|
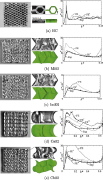
| Comparisons of test and model for crushing of various sandwich core geometries |
|
|