|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
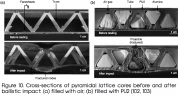
| Pyramidal lattice sandwich cores before and after ballistic impact |
|
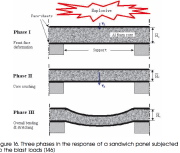
| Response of a sandwich wall to a blast load |
|
| Compression-shear crushing of a honeycomb |
|
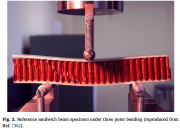
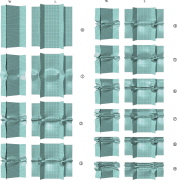
| Three-point bending of honeycomb sandwich structure |
|
| Somewhat simplified model of three-point bending causing localised maximum shear buckling deformation in parts of the honeycomb core |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
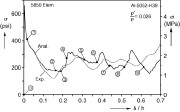
| Shear stress-angle curves including inserts from the finite element models of the honeycomb core |
|
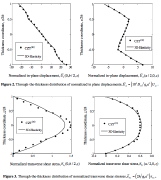
| Through the thickness distributions of various quantities via CZT(m) and 3D elasticity theories |
|
| Honeycomb crushing: 2 views (a,b) of the unit cell that is used for generating the results shown in the following 2 images |
|
| Honeycomb crushing: Comparison of a crushing response from unit cell calculation and experimental one. |
|
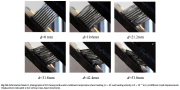
| Honeycomb crushing: Deformed configurations of the unit cell at different degrees of crushing corresponding to numbered bullets on the calculated response shown in the previous image |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
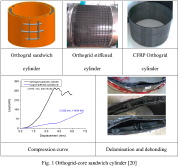
| Axially compressed orthogrid-sandwich, orthogrid, and CFRP-orthogrid cylindrical shells |
|
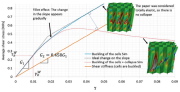
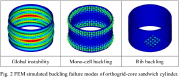
| Global buckling, single-cell buckling and local rib buckling of an axially compressed orthogrid-core sandwich cylindrical shell |
|
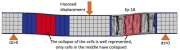
| Typical primary biurcation buckling mode and post-critical response of an axially compressed sandwich column |
|
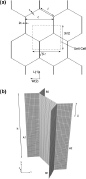
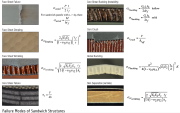
| Failure modes of sandwich structures by Rik Heslehurst |
|
| Failure modes of sandwich structures: Definitions of parameters in the expressions given in the previous image. |
|
|