|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
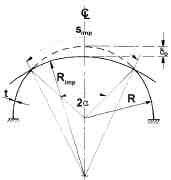
| Hemispherical shell with a "flat" spot. The "imperfect" shell is to be externally pressurized |
|
| How the lower bound of the collapse pressure, Pc, is determined as a function of the flattening amplitude, delta0 |
|
| Molded torispherical shells fabricated of plastic ABS material. The shells have off-axis "flat" spots with geometry of the type shown two slides ago. |
|
| This slide shows the buckled specimens that in the previous slide are shown before testing under external pressure |
|
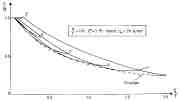
| Comparison between test and theory for the torispherical shells with "flat" regions spanning increasing alpha (increasing delta0) |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
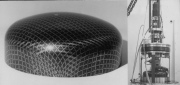
| Finite element model of externally pressurized torispherical shell with small "flat" spot |
|
| Buckled plastic externally pressurized, meridionally stiffened torispherical shell |
|
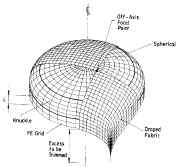
| 350 mm diameter laminated composite torispherical shell fabricated by draping. The shell is to be tested under uniform external pressure |
|
| How the draping is done and modeled for the fabricated specimen shown in the previous slide |
|
| Failure diagram of perfect externally pressurized torispherical shells |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
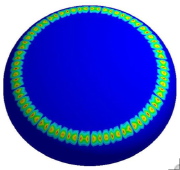
| Linear buckling mode of an internally pressurized torispherical pressure vessel head |
|
| Internally pressurized torispherical vessel |
|
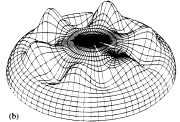
| Typical post-buckling pattern of an internally pressurized torispherical or ellipsoidal steel or aluminaum pressure vessel head |
|
| Axisymmetric elastic-plastic deformation of an internally pressurized ellipsoidal shell predicted by BOSOR5 |
|
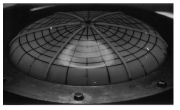
| Post-buckling of an internally pressurized torispherical pressure vessel head from ANSYS finite element model |
|
|