|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Nonlinear generalized load-generalized deflection curve with Riks-like path following |
|
| Modification of nonlinear continuation strategy for the determination of equilibrium states beyond the limit load |
|
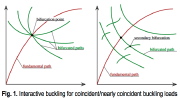
| First and subsequent bifurcations and postbuckling paths from the fundamental nonlinear equilibrium path |
|
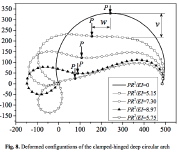
| Large deformation of a deep arch with a downward concentrated load P |
|
| Load-deflection curves for the deep arch shown in the previous image |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
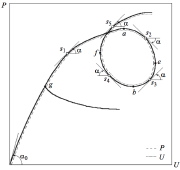
| Branching (bifurcation buckling at g) from nonlinear equilibrium curve and continuation into an extremely nonlinear behavior |
|
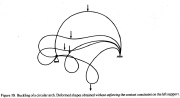
| Very large deflection of a deep arch WITHOUT enforcement of a contact constraint at the left support |
|
| Very large deflection of a deep arch WITH enforcement of a contact constraint at the left support |
|
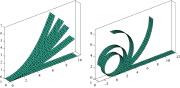
| Deformed configurations at different load levels for end shear force (left) and end moment (right) |
|
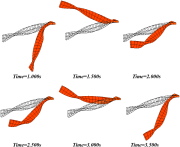
| Large dynamic deformations of a beam with rectangular cross section |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
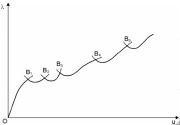
| Successive bifurcation points on a nonlinear equilibrium path in generalized load-generalized displacement space |
|
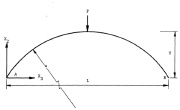
| Fig. 4 Typical arch configuration, with dimensions and concentrated load defined |
|
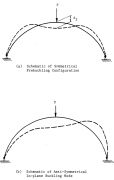
| Fig. 5 Typical in-plane behavior of a simply supported arch (from the same report as the previous slide) |
|
| Fig. 6 Special cross sections of members used in the analysis (from the same report as the previous 2 slides) |
|
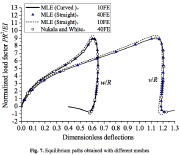
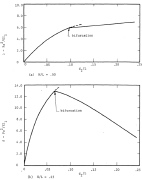
| Fig. 7 Load versus vertical deflection at crown: in-plane buckling of simply supported arches (zero extension of the reference surface) (from the same report as the previous 3 slides) |
|
|