|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
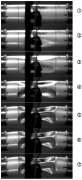
| Fig. 5. Sequence of high speed images that show the dynamic collapse of IMP69 (images taken at 0.16 ms intervals). |
|
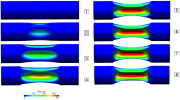
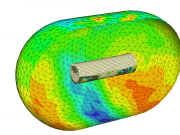
| Fig. 16. Calculated set of deformed configurations for IMP69 with color contours representing the radial displacement. |
|
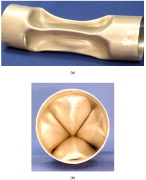
| Fig. 7. Photographs showing the mode 4 (n=4 circumferential waves) collapse of IM69. (a) Side view and (b) end view. |
|
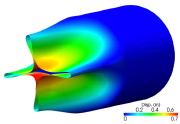
| Fig. 19. Calculated collapsed configuration of shell of IMP69 at the time of first contact ( T " xxx ms) |
|
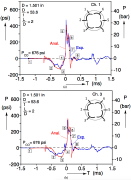
| Fig. 17. Comparison of measured and calculated pressure signals at two sensor locations for IMP69. Numbered bullets correspond to deformed configurations in Fig. 16. |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| ABAQUS water/shell model with "crude" fluid mesh. (Top half of fluid mesh removed for clarity) |
|
| ABAQUS water/shell model with refined fluid mesh. (Top half of fluid mesh removed for clarity) |
|
| Dynamic response of axially oriented strain gage B1 (vertical axis) as a function of time (seconds, horizontal axis) |
|
| Dynamic response of underwater cylindrical shell and water to an explosion |
|
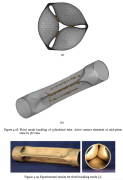
| A submerged long cylindrical shell subject to an underwater explosion energetic enough to cause complete collapse of the shell |
|
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
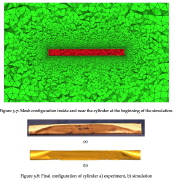
| Comparison of the final state of a somewhat shorter test specimen from theory and experiment |
|
| Elements in the design of metal shells in the European Standard on the Strength and Stability, Fifth Edition |
|
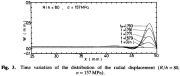
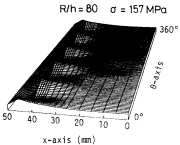
| Creep buckling of an axially compressed cylindrical shell: Axisymmetric pre-buckling deformations versus time of the axially compressed cylindrical shell |
|
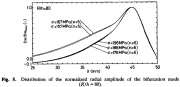
| Creep buckling of a cylindrical shell: Non-axisymmetic bifurcation buckling mode shapes for n = 5 and 6 circumferential waves |
|
| Creep buckling of an axially compresed cylindrical shell: Non-axisymmetric bifurcation buckling mode shape for n = 5 circumferential waves |
|
|